
Photo 2019/04/15
|
|
|
|
In what follows I will simply try to provide the alternatives and give some information about their advantages and disadvantages.
I discuss only clean energy. For example hydrogen can be generated using fossil fuels, but when I discuss hydrogen below it must be taken that I am writing about hydrogen generated using renewable and sustainable methods. There are many potential technologies for obtaining and storing energy sustainably, but only a very few that have been developed to the point that might be called technological maturity. Most methods of sustainably generating electricity are variable, so they must be combined with methods of storing energy. Much has been written about the various sustainable energy developments and energy storage developments, but little has been written comparing their merits. |

|
One of the Toora Wind Farm turbines, early morning; the big shallow Corner Inlet is in the background. Photo 2019/04/15 |
Technology
|
Where does it fit in?
|
|---|---|
Batteries
|
A method of storing energy
|
Compressed air
|
A method of storing energy
|
Fuel cells
|
A method of converting a fuel into electricity (in relation to renewable energy the fuel is hydrogen).
|
Geothermal
|
Methods of using the Earth's heat to generate electricity.
|
Heat banks
|
Substances such as molten salt can be used to store and retrieve energy in the form of heat.
|
Hydrogen
|
Hydrogen can provide a way of storing and moving energy around.
|
Pumped hydropower
|
A method of storing energy
|
Solar photovoltaic (PV)
|
A method of generating electricity.
Solar PV panels convert energy from sunlight directly into electricity.
|
Solar thermal
|
A method of generating electricity.
Solar thermal power stations convert solar radiation (visible and infra-red) into heat and then use the heat to generate electricity (alternatively the heat can be used in industrial processes).
|
Wind turbines
|
A method of generating electricity.
Wind turbines convert energy in wind directly into electricity.
|
|
|
Technology
|
Implications, advantages, disadvantages
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Geothermal
|
There are two main types of geothermal energy generation:
| |||||
Solar photovoltaic (PV)
|
| |||||
Solar thermal
|
| |||||
Wind turbines
|
|
|
|
Technology |
Implications, advantages, disadvantages
|
|---|---|
Batteries
|
Recylability of batteries is a critical question in regard to their environmental sustainability.
Lead-acid batteries are readily and routinely recycled, lithium-ion batteries are a very different matter, while some of the materials can be recovered, the process is expensive, far from all the materials are being recovered, and the lack of purity in the recovered material is problematic.
|
Compressed air
|
There are several ways in which compressed air is used to store energy.
At the time of writing it is very much a developing field of technology.
(For one example, see
Energy Matters, Five alternatives to grid-scale lithium-ion batteries.)
|
Heat
|
There are a number of technologies that store energy in the form of heat. Most forms of energy can be converted into heat with very high efficiency, however converting heat into a more useful form of energy, such as electricity, is much less efficient.
|
Hydrogen
|
There are a number of challenges and inefficiencies involved in the generation, storage and use of hydrogen.
Hydrogen technology is developing. Costs are coming down, efficiencies are improving. It is likely that it will soon become economically viable to generate hydrogen whenever renewable energy is pushing the wholesale price of electricity down.
|
Liquid air
|
This is being used by UK company Highview Power.
At the time of writing it is very much a developing field of technology.
(For one example, see
Energy Matters, Five alternatives to grid-scale lithium-ion batteries.
|
Pumped hydropower
|
This is a very mature technology.
|
Raising and lowering large masses
|
At the time of writing this is very much a developing field of technology.
|
|
|
| Tesla battery degradation |
|---|
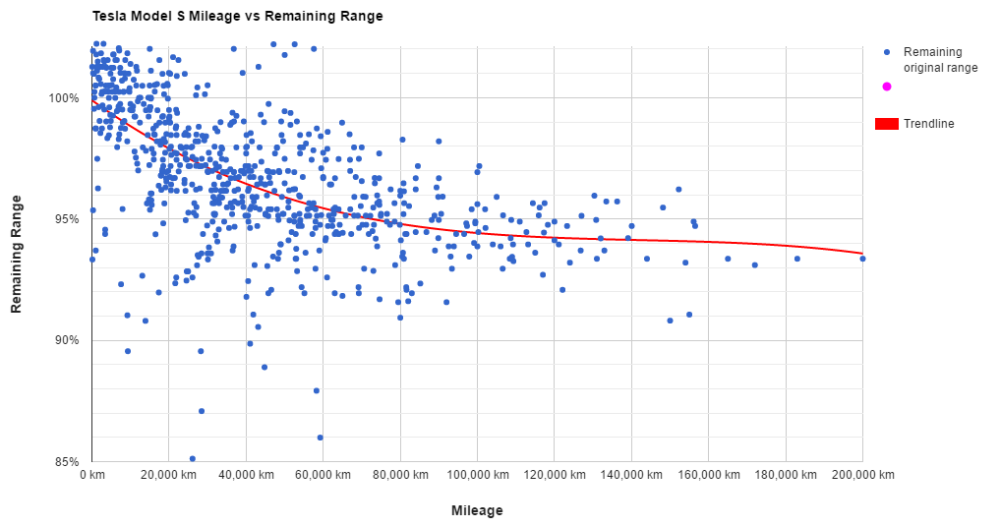
|
The graph above suggests that the capacity of most Tesla car batteries degrade by about 6% after 120,000 kilometres of travelling (the equivalent of about 240 full discharge/recharge cycles) and then degrade hardly at all after that.
Since the greatest distance covered by any of the Teslas involved in the study was 200,000 kilometres extrapolating beyond that involves risk, but the trend line is very suggestive; perhaps the batteries will still have a high capacity at 500,000 kilometres (the equivalent of about 1000 full discharge/recharge cycles) or more? Only time and more research will tell. |
I suppose a more demanding test of batteries will be in utility-scale batteries on the grid where they go through many charging and discharging cycles every day.
This graph records power going into utility-scale batteries (charging - light blue) and coming out of (discharging - dark blue) in the Australian state of South Australia. It shows that the batteries switched between charging and discharging many times during the day. There is no reason to believe that this day was atypical. I believe there were two such batteries operating at the time, Hornsdale Power Reserve and the Dalrymple battery; several others had been proposed and approved. How long will these batteries last? I suspect that individual cells or groups of cells will be replaced as they fail. The relevant information on the longevity of the components may never be made public. |
|
|
Related pagesRelated pages on external sites...The spiralling environmental cost of our lithium battery addiction; Wired on Energy, by Amit Katwala, 2018/08/05.Environmental Impacts of Renewable Energy Technologies; Union of Concerned Scientists. How will future energy storage work? Five alternatives to grid-scale lithium-ion batteries; Energy Matters 1414 Degrees; a company that is developing molten salt heat storage technology in Australia. The technology is especially suitable in situations in which industrial heat, as well as electricity generation, is required. Green energy: What it is and how it works, based in Texas, USA |
Related pages on this site...Battery or hydrogen vehicles?, sustainabilityBatteries, Pumped Hydro, Transmission: renewable energy generation is variable, how can the intermittency problems be overcome? Electric vehicles: some thoughts Power to gas (P2G) in Australia South Australia's success in adopting renewable energy Sustainable energy and environment; concentrating mainly on wind and solar photovoltaic |
|
|
|
|